Union is a used defined data type used to store data under unique variable namea at single memory location.
Union is similar to that of structure. Syntax of union is similar to structurel. But the major Difference between structure and union is 'storage'. In structures, each member has its own storage location, whereas all the members of union use the same location. Union contains may mebers of different types, it can handle only one member at a time.
To declare union data type, 'Union' keyword is used.
Union holds value for one data type which requires larger storage among thier members.
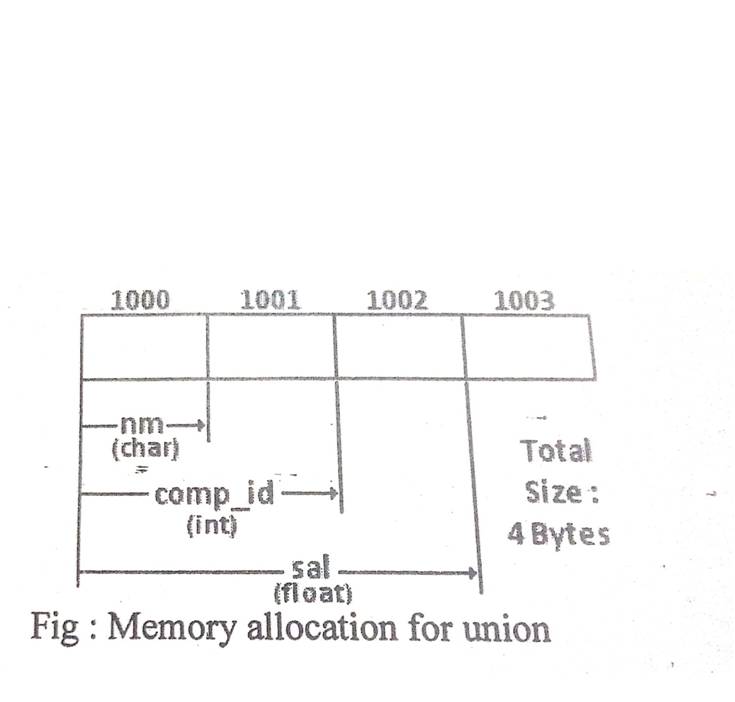
union union_name { < data_type > element1; < data_type > element2; < data_type > element3; }union_variable; Example: union techno { int comp_id; char name; float sal; }tch;
In above example, it declares tch variable of type union. The union certain three members as data type of int, char, float. We can use only one at a time.
* Memory Allocation:

To access union members, we can use the following syntax:
tch.comp_id; tch.name; tch.sal; #include< stdio.h > #include< conio.h > union techno { int id; char name; }tch; void main() { clrscr; printf("\n\t Enter developer id:"); scanf("%d", &tch.id); printf("\n\t Enter developer name:"); scanf("%d", &tch.name); printf("\n\t Developer ID: %d", tch.id); //Garbage printf("\n\t Developed By: %s", tch.name); getch(); } Output: Enter developer id : 101 Enter developer name : technowell Developer ID : 25972 Developed By : technowell